- Sectors
- Aerospace & Defense
- Big science
- Fintech
- Insights
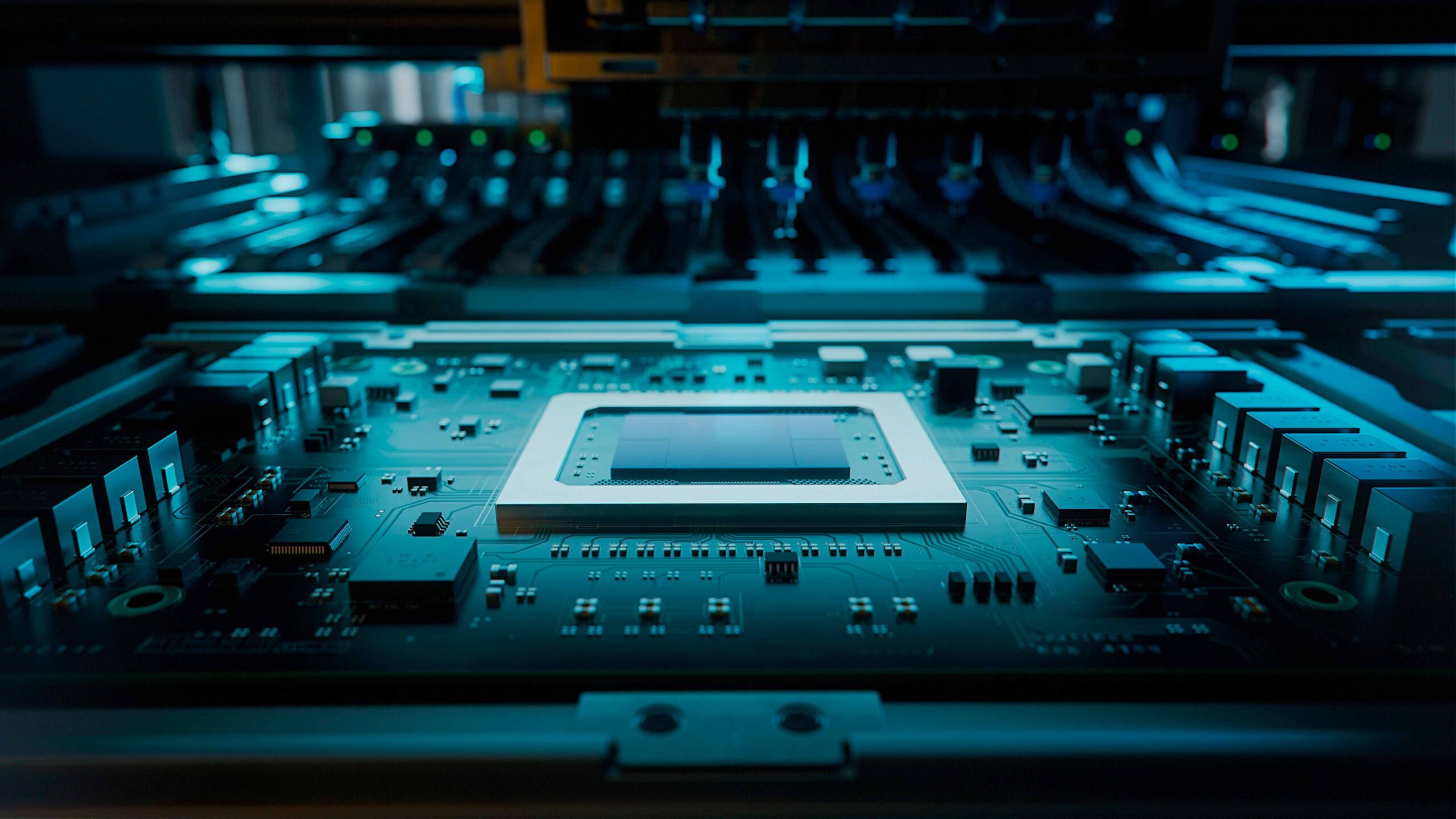
Basic electronics, understood as the study of the fundamental components and circuits that control the flow of electric current, has been a fundamental pillar in the development of modern technology, with roots that extend from the first studies on electricity in the 18th century to the creation of the transistor in the 20th century by the American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley.
From simple elements such as resistors, capacitors, diodes and transistors, a wide range of devices and systems have been developed that form the basis of modern technology, such as radios, televisions and computers.
In the second half of the 20th century, advanced electronics emerged as a natural evolution of basic electronics. The miniaturization of electronic components and the increase in processing capacity led to the creation of high-density integrated circuits and advanced microprocessors. In addition, the development of nanotechnology and new materials such as graphene further boosted this field, enabling applications in diverse areas such as biomedicine, flexible electronics and advanced computing.
Advanced electronics encompasses a wide range of sub-disciplines and applications, characterized by the use of advanced design techniques, innovative materials and novel approaches for improving the performance, efficiency and functionality of electronic devices. Some of the key aspects of advanced electronics are:
Multiple fields benefit today from the advance of advanced electronics. In our blog we would like to highlight some of the most important ones:
With the continuous development of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), quantum computing, and nanotechnology, advanced electronics is emerging as a key player. It is already participating in the revolution of multiple sectors and will undoubtedly play a crucial role in technological transformation, offering us a more interconnected and automated future, with enormous potential for improving quality of life and efficiency.
However, there are still several challenges that advanced electronics has to face. To highlight some of them are:
ARQUIMEA Research Center, the research center of the ARQUIMEA group located in the Canary Islands, has an orbital dedicated to research in the field of Electronics with research lines in miniaturization of electronic systems or the development of state-of-the-art inertial optical systems.
In addition, all the projects of ARQUIMEA Research Center belong to the QCIRCLE project, co-financed by the European Union and whose objective is the creation of a center of scientific excellence in Spain.

“Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.”