- Sectors
- Aerospace & Defense
- Big science
- Biotechnology
- Fintech
- Insights
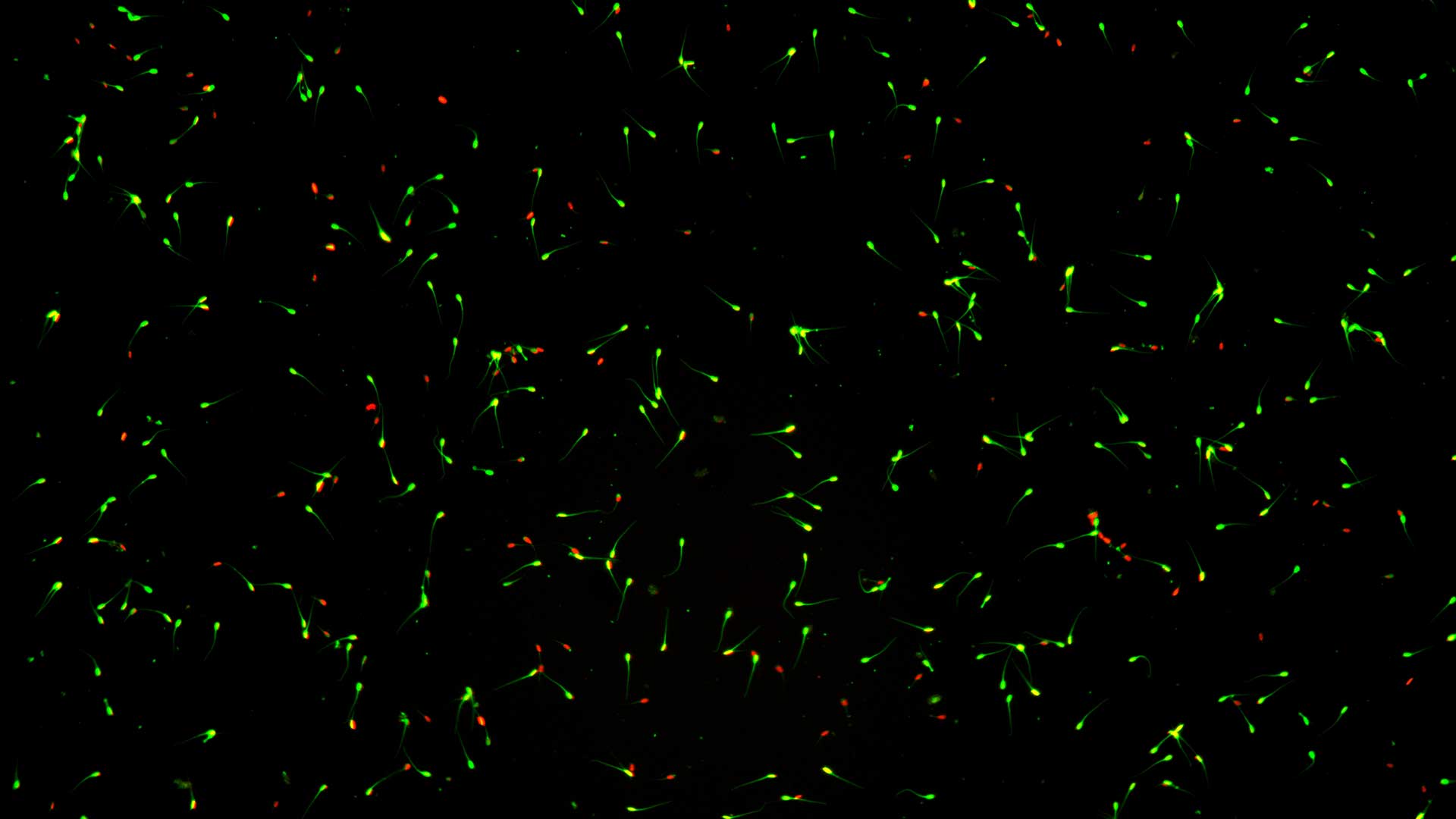
When it comes to animal reproduction, maintaining semen quality over time is a critical process for reproductive success. When we dilute sperm in a specific formulation to protect it during transport and storage, it is essential that the fertilizing capacity of the sperm is preserved. Therefore, the quality of the semen extender used will have a direct impact on fertility results.
Faced with this challenge, ARQUIMEA’s agrotech area, in collaboration with the CSIC, developed a research project with the aim of improving the classic extender formulas, analyzing them by means of cutting-edge technologies that did not exist when the first formulations were developed, or were not so accessible.
Although parameters such as pH or Osmolarity are still taken into account, we can now include additional analyses such as, for example, measuring vitality by fluorescence thanks to fully automated equipment, having more precise and objective kinetic parameters, or analyzing cell metabolism results in real time.
Cellular metabolism analysis technology has recently made great advances, becoming much more accessible and allowing real-time detection of changes in cellular energy consumption.
Thanks to this technology, we are now able to characterize sperm metabolism and quantify the energy consumed by spermatozoa, both by oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis, as well as to observe how sperm behave in stressful situations, such as lack of energy or accumulation of toxic metabolites in the environment.
By means of these state-of-the-art technologies, the ARQUIMEA and CSIC research team carried out an exhaustive characterization of sperm metabolism. With the aim of preserving the fertilizing capacity of spermatozoa for a longer period of time, they evaluated different semen extenders with variations in composition and sugar concentration.
These components, beyond their function as an essential energy source during preservation, play a crucial role in maintaining the osmotic pressure of the medium, a determining factor in preserving the integrity of the cell membrane.
The results of the project not only provided a wealth of information for adjusting the concentration of the different extender components, but also subjected these new formulations to a battery of additional tests to evaluate their efficacy:
All these checks were carried out over a period of 8 days, which is the maximum duration contemplated for the use of the long-acting diluent. Those formulas that gave the best results were subjected to field tests with inseminations.
From the results obtained in both the in vitro and field tests, an index for each extender was elaborated taking into account all these variables.
In certain scenarios, the weighting of the parameters varies depending on the intended use of the extender, whether for short, medium or long duration periods. This adaptability reflects careful consideration of the specific characteristics needed for each application.
In other cases, the weight assignment to a parameter in the formulation may be based not only on the duration of storage, but also on specific correlations identified with observed in vivo results.
ARQUIMEA, together with CSIC, observed that membrane quality and acrosome integrity stood out as the most crucial factors for better fertility results. Therefore, when formulating their semen extenders, they developed a formula that prioritized membrane vitality and acrosome integrity after dilution over other aspects.
With these study results, ARQUIMEA Technology reformulated ACROMAX, its long-acting extender based on this fundamental premise: the quality of the sperm membrane is related to better fertility results in the field. This is how ACROMAX PLUS was born, a extender capable of maintaining the integrity of the membrane for longer and, therefore, being able to obtain better fertility results.
Their desire to improve fertility results has generated from new compositions and combinations of sugars to new antibiotic-free extenders, novel seminal freezing methods or experimental compounds that can act as cryoprotectants to work with frozen semen.